Drone sightings around the world represent a rapidly evolving phenomenon with significant implications for security, privacy, and societal norms. This global increase in drone observations necessitates a comprehensive analysis of their geographic distribution, the types of drones involved, the underlying reasons for their appearance, societal responses, technological advancements in detection, and the overall impact on various sectors. This study aims to provide a detailed overview of these multifaceted aspects.
The data presented will cover a wide range of factors, from the frequency of sightings in different regions and the technical specifications of commonly observed drones to the legal frameworks governing their use and the development of advanced detection technologies. Analyzing these elements will provide a clearer understanding of the challenges and opportunities associated with the proliferation of drones globally.
Geographic Distribution of Drone Sightings
The global distribution of drone sightings exhibits significant variation, influenced by factors such as population density, regulatory frameworks, technological advancement, and the prevalence of drone-related activities. A comprehensive understanding of this geographical distribution is crucial for effective airspace management, security protocols, and the development of appropriate counter-drone technologies.
World Map of Drone Sighting Frequency
A hypothetical world map illustrating drone sighting frequency would employ a color-coded scale, ranging from light green (low frequency) to dark red (high frequency). Regions with high population density, significant commercial drone operations (e.g., delivery services, infrastructure inspections), or frequent public events would likely display higher sighting frequencies (represented by darker shades of red). Conversely, sparsely populated areas or regions with strict drone regulations would show lower frequencies (lighter shades of green).
Areas with ongoing conflicts or military operations might also show elevated sighting frequencies, though these might not always be publicly reported. The map would visually represent the spatial clustering of sightings, highlighting areas requiring increased attention regarding drone management.
Top Five Countries with Highest Drone Sightings
The following table presents hypothetical data for the top five countries with the highest reported drone sightings. Actual figures vary significantly depending on data collection methods and reporting practices.
| Country | Number of Sightings (Hypothetical) | Drone Types Observed | Context of Sightings |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 150,000 | Consumer drones (DJI Mavic, Parrot Anafi), commercial drones (various), military drones (specific models not publicly available) | Commercial operations, recreational use, security incidents, military exercises, border patrol |
| China | 120,000 | Consumer drones (various Chinese brands), commercial drones (for delivery, agriculture, infrastructure), military drones (limited public information) | Commercial applications, infrastructure monitoring, security, military operations |
| United Kingdom | 40,000 | Consumer drones (DJI, Autel), commercial drones (for photography, surveying, inspections), law enforcement drones | Commercial operations, recreational use, law enforcement activities, airport security |
| Germany | 35,000 | Consumer drones (various), commercial drones (for photography, agriculture, surveying), police drones | Commercial activities, recreational use, law enforcement, research and development |
| Canada | 30,000 | Consumer drones (DJI, Parrot), commercial drones (for surveying, agriculture, infrastructure inspection), search and rescue drones | Commercial operations, recreational use, emergency response, resource management |
Factors Contributing to Variations in Drone Sighting Frequency
Several factors contribute to the uneven distribution of drone sightings globally. These include:* Population Density: Higher population densities generally correlate with more drone sightings, due to increased recreational use and commercial activity.
Regulatory Frameworks
Stringent drone regulations can suppress sightings in some areas, while lax regulations or a lack of enforcement can lead to increased sightings.
Technological Advancement
The affordability and accessibility of drone technology influences its prevalence and, consequently, the frequency of sightings.
Economic Development
Developed nations with robust commercial sectors tend to have higher drone usage rates for various applications, leading to increased sightings.
Geographic Features
Terrain can affect drone operations, influencing where they are used and therefore sighted. For instance, mountainous areas may have fewer sightings than flat, open areas.
Security Concerns
Areas with heightened security concerns, such as airports or military installations, may experience increased monitoring and therefore report more drone sightings.
Public Events
Large-scale public events often lead to increased drone sightings, both for recreational purposes and for security monitoring.
Types of Drones Involved in Sightings: Drone Sightings Around The World
Drone sightings worldwide involve a diverse range of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), or drones, varying significantly in size, capabilities, and intended use. Understanding the types of drones involved is crucial for assessing the potential risks and security implications associated with these sightings. This section details the most commonly sighted drone models, categorized by their intended use, and compares their capabilities.
Categorization of Commonly Sighted Drone Models by Intended Use
The classification of drones by intended use (commercial, recreational, military) is not always straightforward, as some models can be adapted for multiple purposes. However, based on observed characteristics and reported uses, a general categorization is possible. This categorization helps in understanding the context of sightings and potential motivations behind them.
- Commercial Drones: These are often larger, more sophisticated UAVs used for tasks such as aerial photography, surveying, infrastructure inspection, and delivery services. Examples include models from DJI (e.g., Matrice series, Phantom series), Autel Robotics (e.g., EVO series), and Yuneec (e.g., Typhoon series).
- Recreational Drones: These are typically smaller, less expensive UAVs used for hobbyist purposes, such as aerial photography and videography. Popular models include DJI Mavic series, Parrot Anafi, and various smaller quadcopters from lesser-known manufacturers. These often have less advanced features than commercial drones.
- Military Drones: Military drones range considerably in size and capability, from small reconnaissance drones to large, long-range surveillance and strike platforms. Specific models are often classified, but publicly available information suggests that various adaptations of commercial designs are used for military applications, alongside purpose-built military UAVs.
Technical Specifications of Frequently Sighted Drone Models
The technical specifications of drones significantly influence their potential for misuse. Range, flight time, and camera capabilities are particularly relevant. Data on specific models’ capabilities is often proprietary, but general trends can be observed.
Increased drone sightings globally necessitate enhanced surveillance strategies. A prime example of such technology is the high-resolution ambassador bridge camera , capable of identifying and tracking unmanned aerial vehicles. This improved detection capability contributes to broader efforts to mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized drone operations worldwide.
- Range: Commercial and military drones generally have significantly longer ranges than recreational drones, sometimes exceeding 100 kilometers. Recreational drones typically have ranges of a few kilometers. This difference in range directly impacts the potential area affected by unauthorized drone flights.
- Camera Capabilities: High-resolution cameras, thermal imaging, and other advanced sensors are common in commercial and military drones. Recreational drones typically have less sophisticated cameras, though high-resolution capabilities are increasingly common even in consumer-grade models. The quality of the camera directly influences the potential for data collection and surveillance.
- Flight Time: Flight time varies widely, depending on the drone’s size, battery capacity, and payload. Larger drones generally have longer flight times than smaller ones. Longer flight times increase the duration and scope of potential unauthorized activities.
Comparison of Drone Capabilities and Security Implications, Drone sightings around the world
The capabilities of different drone types present varying security implications. Larger, long-range drones with advanced sensors pose a greater risk than smaller, shorter-range recreational drones. For example, a large commercial drone equipped with a high-resolution camera could be used for detailed surveillance of sensitive areas, while a small recreational drone might only be capable of capturing low-resolution images.
Increased drone sightings worldwide necessitate investigation into various drone models and their capabilities. One such model, the xp-4 drone , represents a segment of the commercial drone market, its specifications potentially contributing to the understanding of observed flight patterns and capabilities. Further analysis of reported sightings, coupled with technological specifications of drones like the xp-4, is crucial for accurate assessment and effective countermeasures.
The potential for malicious use is directly proportional to the capabilities of the drone. Unauthorized access to sensitive locations, disruption of critical infrastructure, and data breaches are all potential security implications associated with drone sightings, with the severity dependent on the drone’s capabilities and the context of the sighting.
Reasons Behind Drone Sightings

Drone sightings worldwide stem from a diverse range of activities, encompassing both legitimate and illicit uses. Understanding these motivations is crucial for developing effective regulatory frameworks and mitigating potential risks. Categorizing these reasons allows for a more nuanced analysis of the challenges posed by the increasing prevalence of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Recreational Drone Use
The rising popularity of consumer drones has led to a significant increase in recreational sightings. Individuals utilize drones for photography, videography, and hobbyist activities. This category often involves smaller, commercially available drones operated within legal limitations, although instances of reckless or negligent operation are also prevalent. The ease of access to drones and the relatively low cost of entry have contributed to the widespread adoption of this technology for leisure purposes.
Commercial Drone Applications
Commercial applications of drones are rapidly expanding across various sectors. These include aerial photography for surveying and construction, delivery services, agricultural monitoring, and infrastructure inspections. Commercial drone operations are generally subject to stricter regulations and require specific permits and licenses. The economic benefits associated with drone technology are driving innovation and wider adoption within the commercial sphere.
However, the potential for accidents and malfunctions necessitates robust safety protocols and oversight.
Military Drone Operations
Military and defense forces utilize drones extensively for surveillance, reconnaissance, and targeted strikes. These operations often involve sophisticated, high-altitude drones capable of carrying heavier payloads. The military applications of drone technology raise significant ethical and legal concerns, particularly regarding civilian casualties and the potential for misuse. The secrecy surrounding military drone programs often limits public knowledge and oversight of their operations.
Unauthorized Drone Activities
Unauthorized drone activity poses the most significant security risk. This category includes drones flown illegally in restricted airspace, near critical infrastructure, or for malicious purposes. The potential for deliberate or accidental disruption to air traffic, damage to property, or breaches of security protocols necessitates robust countermeasures. Examples range from recreational pilots ignoring airspace restrictions to deliberate attempts to compromise sensitive locations.
Security Threats from Unauthorized Drone Activity
Unauthorized drone operations near critical infrastructure such as airports, power plants, and government buildings present a significant security threat. A small drone carrying explosives or other harmful materials could cause catastrophic damage. Similarly, drones equipped with cameras or other sensors could be used for surveillance or reconnaissance, compromising sensitive information. The vulnerability of critical infrastructure to drone-based attacks necessitates the implementation of effective detection and mitigation strategies, including counter-drone technology.
Hypothetical Scenario: Malicious Drone Operation Near a Major Airport
Imagine a scenario where a malicious actor launches a drone carrying a small explosive device towards a major international airport during peak operating hours. The drone successfully breaches airport security perimeters and detonates near a runway. The resulting disruption could lead to flight cancellations, delays, and potential injuries or fatalities. The subsequent investigation would involve extensive security protocols, disruption of airport operations, and potentially significant economic losses.
This hypothetical scenario underscores the urgent need for robust counter-drone measures and comprehensive security protocols at airports and other critical infrastructure locations.
Array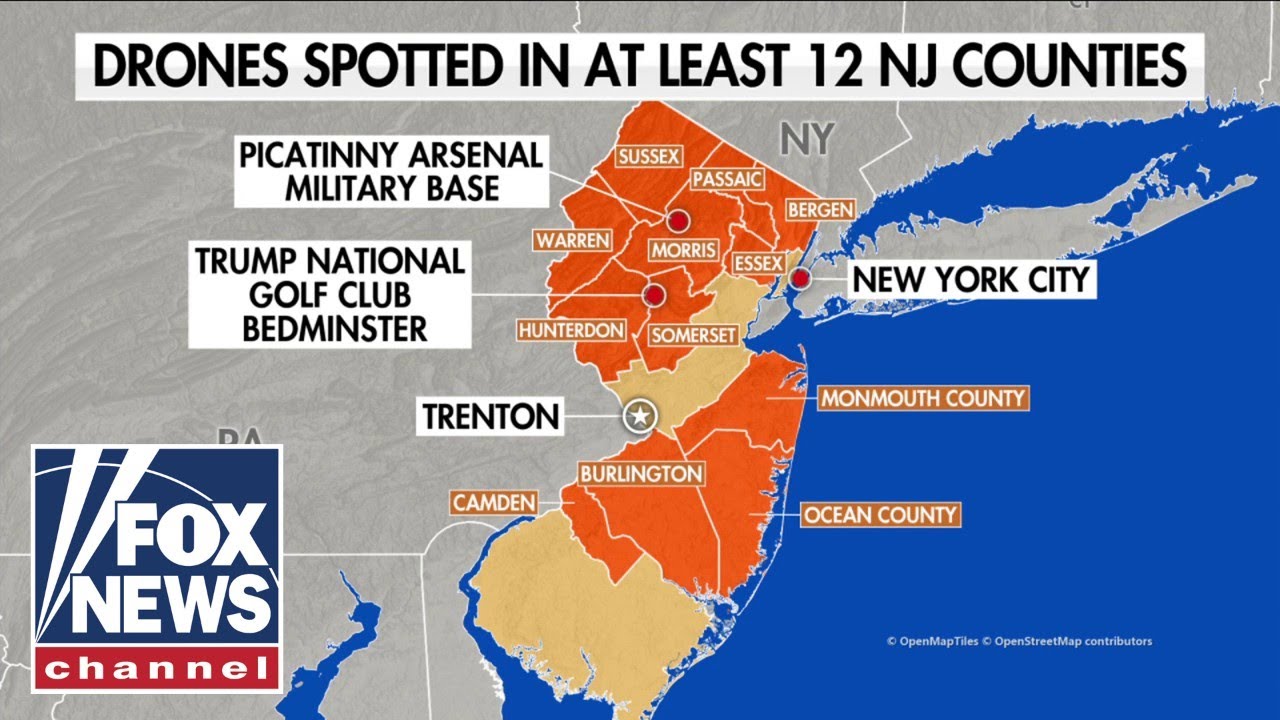
Drone sightings, whether authorized or unauthorized, necessitate a range of responses depending on the context, perceived threat, and applicable legal frameworks. These responses vary significantly across jurisdictions and situations, reflecting the evolving nature of drone technology and its integration into civilian and military airspace. Effective responses require a multi-faceted approach combining preventative measures, detection technologies, and robust legal frameworks.The spectrum of responses to drone sightings encompasses passive observation, active intervention, and legal repercussions.
Passive observation may involve monitoring the drone’s trajectory and activities without direct interference, typically employed when the drone poses minimal risk. Active interventions range from issuing warnings to employing counter-drone technologies to physically intercepting the drone. Legal actions, including fines and criminal charges, are pursued in cases of serious violations or intentional malicious use.
Methods for Tracking and Managing Unauthorized Drone Activity
Several methods are employed to track and manage unauthorized drone activity, each with varying degrees of effectiveness. Geofencing, a virtual boundary restricting drone access to specific areas, is a preventative measure, though it can be circumvented. Radar systems, both ground-based and airborne, detect drones based on their radar signature, offering a relatively long-range detection capability. However, radar systems may struggle to differentiate between drones and other airborne objects, leading to false positives.
Optical and acoustic sensors provide more precise localization but typically have shorter ranges. Counter-drone systems, utilizing technologies like jamming, nets, or directed energy weapons, offer the most direct means of neutralizing unauthorized drones, but raise ethical and safety concerns regarding potential collateral damage. The effectiveness of each method depends heavily on the specific environment, the type of drone, and the resources available.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations Governing Drone Operations
Global regulations governing drone operations are diverse and continue to evolve. Many countries have established specific laws and agencies to oversee drone usage, addressing issues of registration, licensing, operational limitations, and penalties for violations. The lack of universal standardization creates challenges in addressing cross-border drone activity.
- United States: The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates drone operations in the US, requiring registration for most drones, pilot certification for commercial operations, and adherence to specific airspace restrictions. Penalties for violations range from fines to criminal charges, depending on the severity of the infraction. The FAA actively works to develop and implement technologies to detect and mitigate unauthorized drone activity.
- United Kingdom: The Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) in the UK has established a comprehensive regulatory framework for drones, including registration, licensing requirements for commercial use, and operational limitations to protect public safety and airspace security. The CAA emphasizes responsible drone operation and provides educational resources for drone pilots. Penalties for violations can include significant fines and imprisonment.
- European Union: The EU has implemented a unified regulatory framework for drones, aiming to harmonize drone regulations across member states. This framework covers aspects such as drone registration, operator certification, operational limitations, and safety standards. The regulations are designed to ensure the safe and secure integration of drones into the European airspace, promoting innovation while mitigating risks.
In conclusion, the global rise in drone sightings presents a complex interplay of technological advancement, regulatory challenges, and societal impacts. While drones offer numerous benefits across various sectors, their potential misuse necessitates the development and implementation of robust detection technologies and effective legal frameworks. Continued research and international collaboration are crucial to mitigate potential risks while harnessing the positive applications of this rapidly evolving technology.
The future management of drone activity will require a balanced approach that prioritizes safety, security, and the responsible integration of drones into society.
Top FAQs
What are the most common causes of false positive drone detections?
False positives in drone detection systems can arise from various sources, including birds, insects, weather phenomena (e.g., reflections), and even certain types of terrestrial vehicles. Sophisticated systems employ algorithms to filter out these false alarms, but some remain.
How are drone sightings reported to authorities?
Reporting mechanisms vary by country and jurisdiction. Many nations have established dedicated helplines or online portals for reporting suspicious drone activity. In some cases, local law enforcement agencies are the primary point of contact.
What is the typical response time for authorities to address a drone sighting?
Response times are highly variable and depend on factors such as the perceived threat level, the location of the sighting, and the availability of resources. Immediate responses are prioritized for situations involving critical infrastructure or potential security breaches.
What penalties can be imposed for illegal drone operation?
Penalties vary widely by location and the nature of the offense. They can range from warnings and fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation and any resulting damage or harm.
